

#Rpp dan silabus pai sma kurikulum 2013 smk download#
Download Contoh Jadwal Pelajaran Sekolah SD SMP SMA SMK Pada Kurikulum 2013 Dan Kurikulum KTSP. (K3) :Memahami dan menerapkan pengetahuan faktual, konseptual, prosedural dalam ilmu pengetahuan, teknologi, seni, budaya, dan humaniora dengan wawasan kemanusiaan, kebangsaan, kenegaraan, dan peradaban terkait fenomena dan kejadian, serta menerapkan pengetahuan prosedural pada bidang kajian yang spesifik sesuai dengan bakat dan minatnya untuk memecahkan masalah (K4) :Mengolah, menalar, dan menyaji dalam ranah konkret dan ranah abstrak terkait dengan pengembangan dari yang dipelajarinya di sekolah secara mandiri, dan mampu menggunakan metoda sesuai kaidah keilmuan. Format File dan info Berikut ini adalah kumpulan dari berbagi sumber tentang.
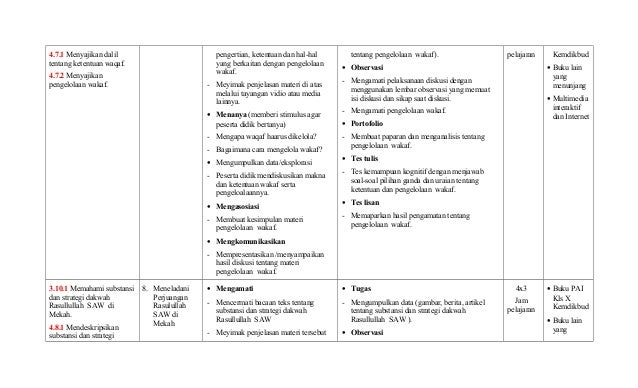
Kompetensi Inti : (K1) : Menghayati dan mengamalkan ajaran agama yang dianutnya (K2) : Mengembangkan perilaku (jujur, disiplin, tanggungjawab, peduli, santun, ramah lingkungan, gotong royong, kerjasama, cinta damai, responsif dan pro-aktif) dan menunjukan sikap sebagai bagian dari solusi atas berbagai permasalahan bangsa dalam berinteraksi secara efektif dengan lingkungan sosial dan alam serta dalam menempatkan diri sebagai cerminan bangsa dalam pergaulan dunia. However a deeper soil depth increased the weight of solids and the soil moisture conditions in the slope consequently increasing the pore water pressure causing slope failure. A shallow soil depth resulted in greater discharge volume and a lower peak pore water pressure during the major rainfall event, and consequently the slope failure tends not to occur. In addition, the thickness of soil is also a significant parameter in slope stability analysis. Under weaker storm conditions, slope failure tends not to occur when the surface soil has a relatively large ESP value. In this manner, a relatively large surface layer ESP value contributes to delaying slope failure. Consequently, the increase in pore water pressure in the subsurface layer is also delayed. Results showed that when the surface soil of a slope has a relatively large ESP value, it has a greater capacity for holding rainwater, and therefore delays rainwater infiltration into the subsurface layer. This model is then used to analyze the effects of the soil porosity parameters (i.e., saturated soil water content θ s and effective soil porosity (ESP)) and soil thickness on the occurrence of slope failure. In this study, a numerical model was developed to estimate the extent of rainwater infiltration into an unsaturated slope, the formation of a saturated zone, and the change in slope stability. In contrast, few studies have been published on the effects of water retention characteristics on slope stability. Amongst the soil hydraulic properties, the hydraulic conductivity K has been frequently analyzed for its effects on slope stability.

Modeling rainwater infiltration in slopes is vital to the analysis of slope failure induced by heavy rainfall.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
